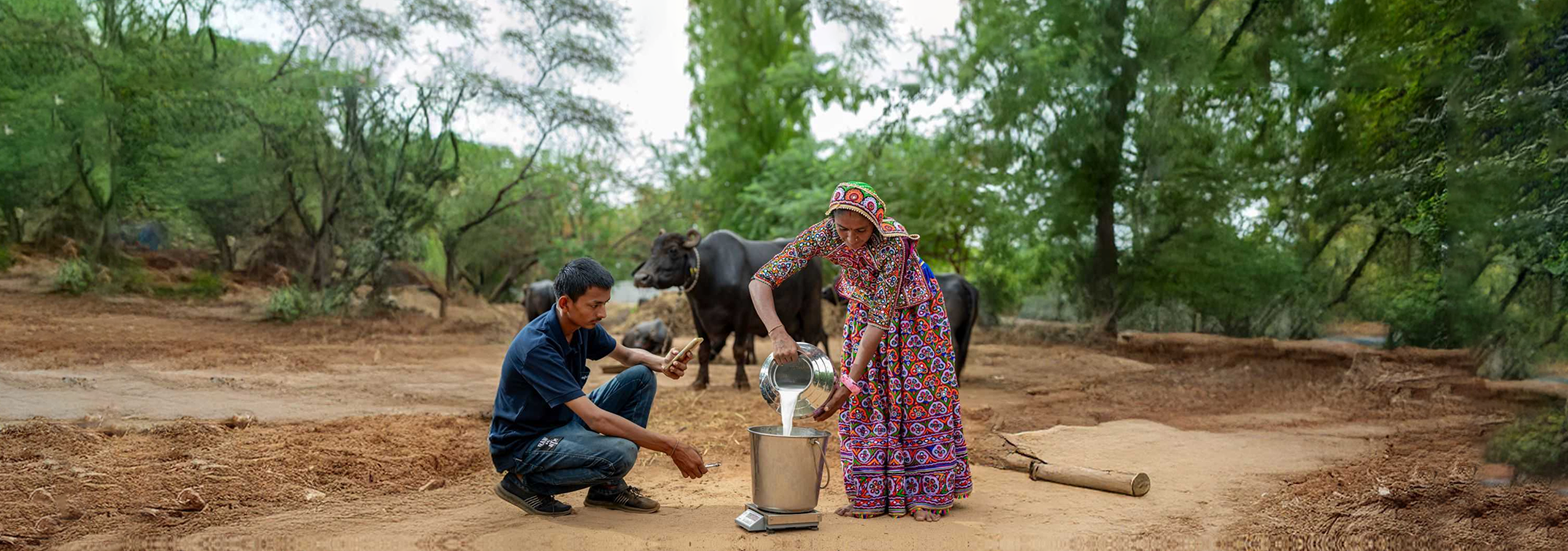
Promoting Fodder Conservation through Silage
- To ensure round the year fodder availability in deficit regions and seasons, preservation of green fodder in the form of silage plays a crucial role.
- Silage is the conserved green fodder having moisture content in the range of 65 to 70 per cent. Fodder crops rich in soluble carbohydrates are ensiled under anaerobic conditions.
- Fodder crops such as maize, sorghum, oats and pearl millet are suitable for silage making.
- Benefits of silage
o Improves productivity and quality of milk
o Inclusion of silage optimizes cost of feeding
o Ensures availability of fodder in lean periods
o Saves labour and time
o Provides scope of increasing cropping intensity
- NDDB provides technical support to dairy cooperatives/ entrepreneurs for establishment of silage-making units and also conducts demonstration and awareness programs for increased silage production and feeding.
- To augment fodder resources in the country, NDDB is striving for exploring possibilities of conserving vegetable and fruit wastes (empty pea pods, mango peel, tomato pomace etc.) in the form of silage.
Promoting Fodder Conservation through Silage
- To ensure round the year fodder availability in deficit regions and seasons, preservation of green fodder in the form of silage plays a crucial role.
- Silage is the conserved green fodder having moisture content in the range of 65 to 70 per cent. Fodder crops rich in soluble carbohydrates are ensiled under anaerobic conditions.
- Fodder crops such as maize, sorghum, oats and pearl millet are suitable for silage making.
-
Benefits of silage
- Improves productivity and quality of milk
- Inclusion of silage optimizes cost of feeding
- Ensures availability of fodder in lean periods
- Saves labour and time
- Provides scope of increasing cropping intensity
- NDDB provides technical support to dairy cooperatives/ entrepreneurs for establishment of silage-making units and also conducts demonstration and awareness programs for increased silage production and feeding.
- To augment fodder resources in the country, NDDB is striving for exploring possibilities of conserving vegetable and fruit wastes (empty pea pods, mango peel, tomato pomace etc.) in the form of silage.