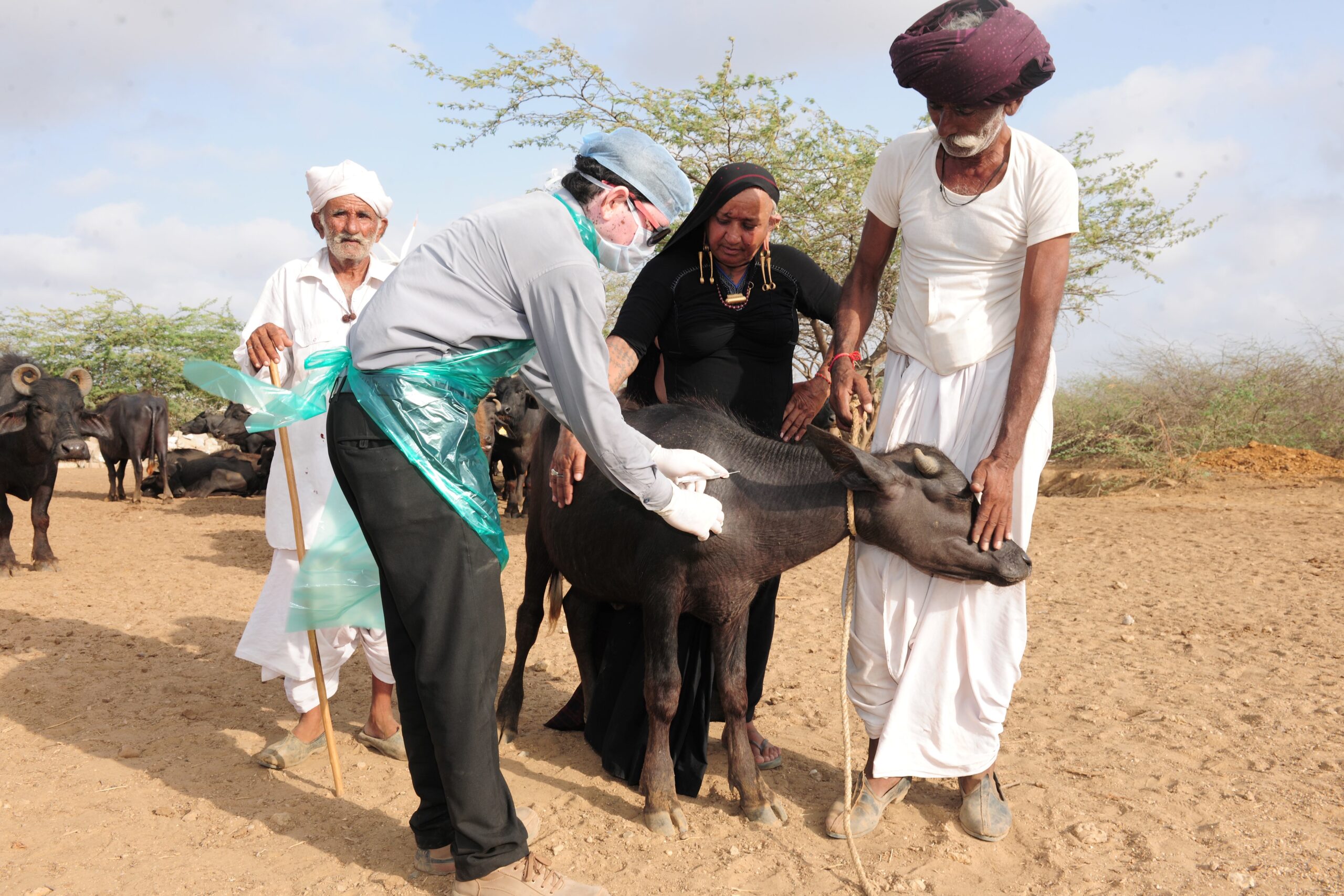
NDDB is implementing a comprehensive One Health model for brucellosis control that creates linkages between animal and human cases. The approach emphasizes identification of infected animals, disinfection of premises, proper disposal of aborted fetuses and placenta. The vaccination is being carried out under the National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP).
The model has facilitated testing of more than 8000 animals and 6,200 humans, with successful treatment of over 138 human brucellosis patients, achieving a 100% recovery rate. This approach demonstrates how addressing animal disease can directly benefit human health.


Carrying out brucellosis vaccination and testing of humans for brucellosis
Disease control through Alternative methods (DCAM)
NDDB is implementing DCAM project since 2017-18 wherein major focus is on improving milk quality and, reducing antimicrobial use (AMU) and antimicrobial resistance (AMR). A total of over 1400 villages in 16 milk unions/producer companies across 8 States are involved in this project. The project has been expanded as the Dairy Integrated Safety and Health Action (DISHA) project from 2025-26 which encompasses comprehensive One Health strategies to reduce the transmission of diseases from animals to humans, thereby protecting public health and livelihoods and, improving food safety.
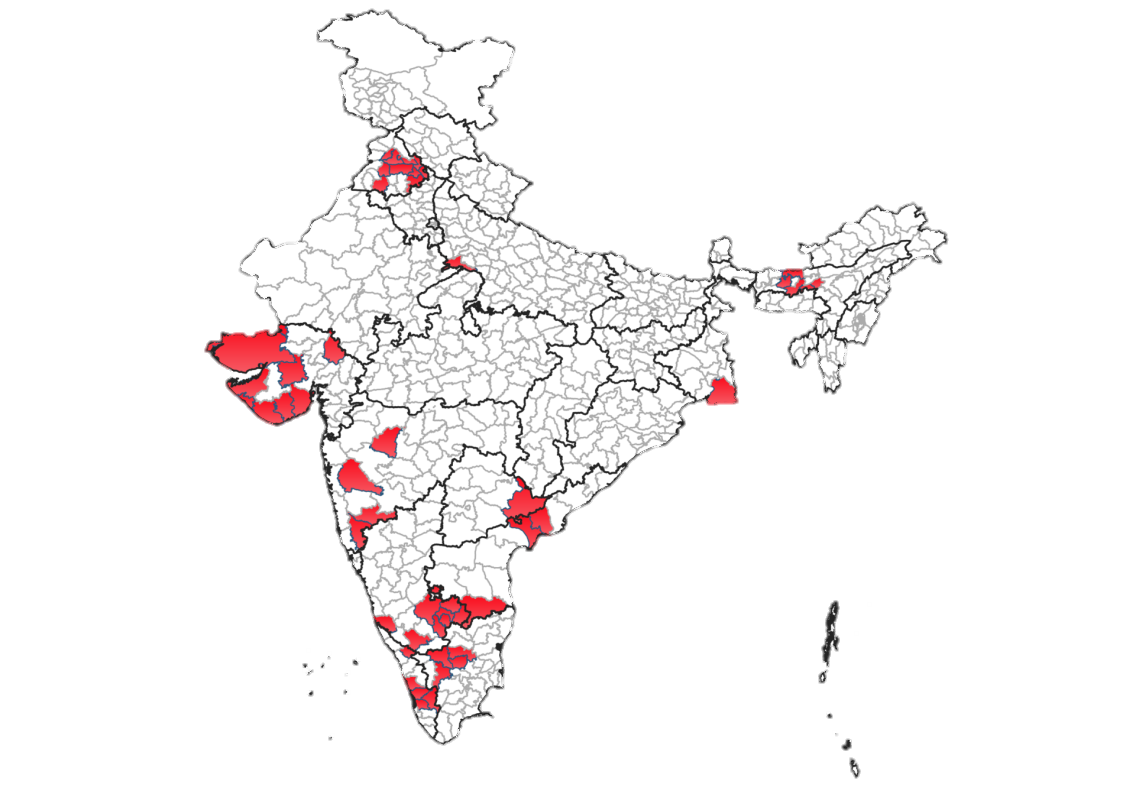

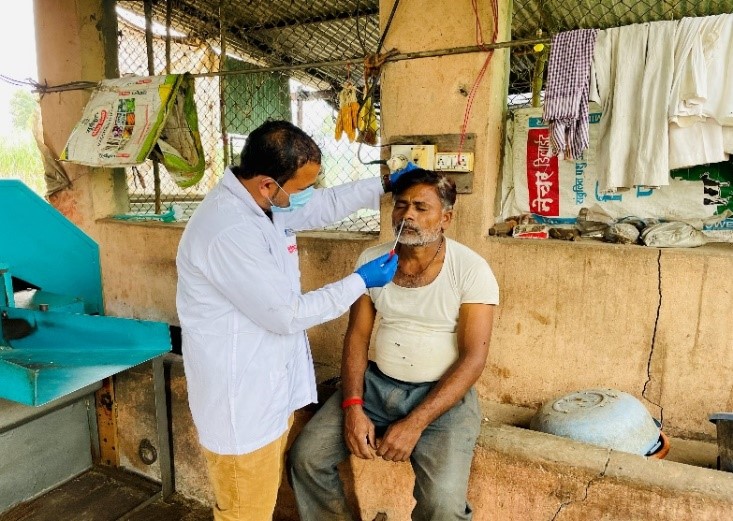

One Health model for Brucellosis Control
NDDB is implementing a comprehensive One Health model for brucellosis control that creates linkages between animal and human cases. The approach emphasizes identification of infected animals, disinfection of premises, proper disposal of aborted fetuses and placenta. The vaccination is being carried out under the National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP).
The model has facilitated testing of more than 8000 animals and 6,200 humans, with successful treatment of over 138 human brucellosis patients, achieving a 100% recovery rate. This approach demonstrates how addressing animal disease can directly benefit human health.